Introduction
The Object.freeze() method is used to freeze the properties of an object. By using Object.freeze() the object does not allow adding a new property, deleting an existing property, or changing a property's value. It is used to make an object immutable.
Example
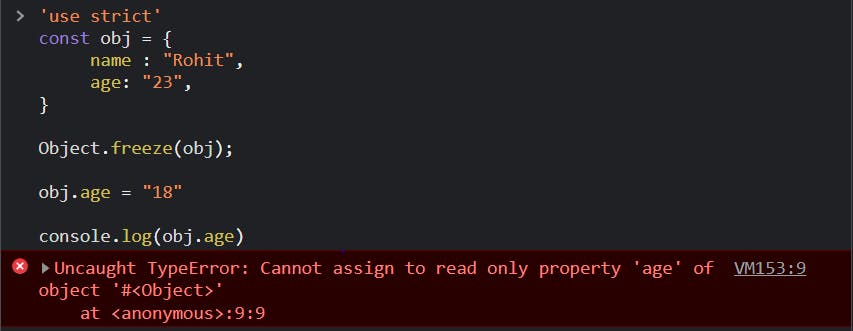
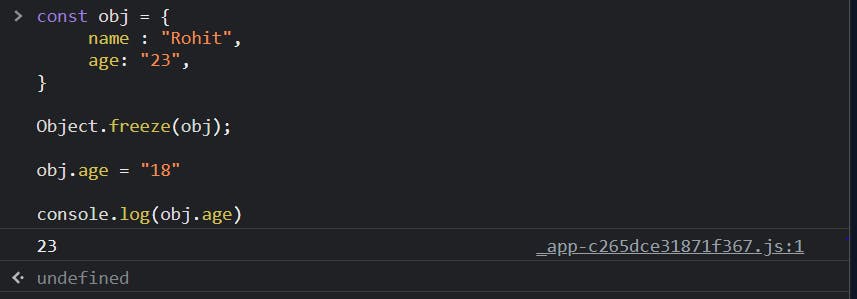
const obj = {
name : "Rohit",
age: "23",
}
Object.freeze(obj);
obj.age = "18"
console.log(obj.age)
// output: 23
So,using Object.freeze() the object becomes immutable.
How to use it?
There are two outcomes when using Object.freeze(), one for strict mode and the other for normal mode.
- In strict mode, making any modification in the frozen object will give typeError, whereas,
- In normal mode, it will ignore the expression.
strict mode
normal mode
Why do we need Object.freeze() ?
Object.freeze() is used when we want to make an object immutable, sometimes we want to limit the mutability of an object, this is quite a common practice in the Object-Oriented Paradigm where the final keyword is used in programming languages like Java.
Limitations.
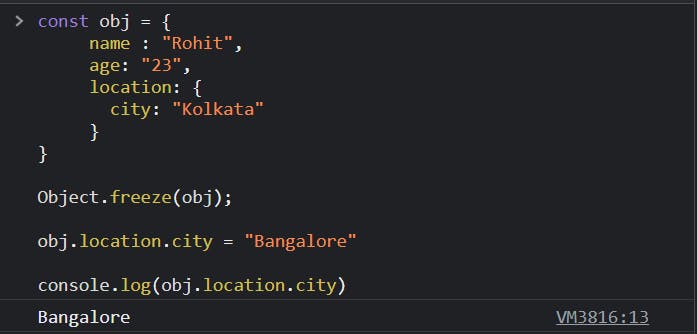
When using Object.freeze(), the object is frozen in a shallow way, i.e. the nested objects are not frozen.
Example
This can be overcome using deep freeze. By looping over each property and freezing each object type property.
function deepFreeze(object) {
// Retrieve the property names defined on object
const propNames = Object.getOwnPropertyNames(object);
// Freeze properties before freezing self
for (const name of propNames) {
const value = object[name];
if (value && typeof value === "object") {
deepFreeze(value);
}
}
return Object.freeze(object);
}
const obj = {
name: "Rohit",
age: 23,
location: {
city: "Kolkata",
}
};
deepFreeze(obj);
obj.location.city = "Bangalore"
console.log(obj.location.city);
// output: Kolkata
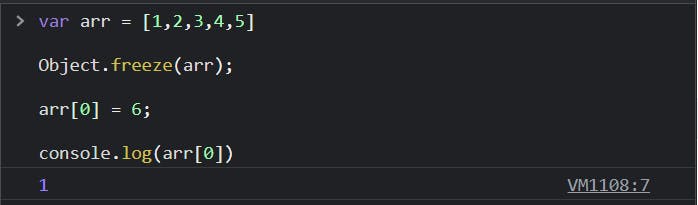
Object.freeze() can also be used on arrays.